Azure AZ-140 practice material sharing and knowledge expansion

I will explain this article in two parts, the content is practical.
- The first part shares the latest Microsoft Azure AZ-140 exam practice materials
- The second part expands the core knowledge points of Azure Virtual Desktop
Test your actual combat effectiveness through online exercises and understand your current true strength. This is the best combat experience to help you improve yourself quickly.
A total of 12 latest Microsoft AZ-140 certification exam practice questions are shared below for free. These question types cover some of the core exam content (Microsoft Certified: Azure Virtual Desktop Specialty).
More importantly! You can register as a Leads4Pass member to get the 202 latest Azure AZ-140 exam practice questions: https://www.leads4pass.com/az-140.html (covering the complete core exam content)
Azure AZ-140 practice material sharing
| From | Number of exam questions | Type | Related | PDF Download |
| Leads4Pass | 12/202 | Free | Microsoft Azure specialty | https://drive.google.com/file/d/1kUXfCoOq_I27R49VgW_Th4L62NS79SsY/view?usp=sharing |
NEW QUESTION 1:
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a web app named mywebapp1. Mywebapp1 uses the address myapp1.azurewebsites.net. You protect mywebapp1 by implementing an Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF). The traffic to mywebapp1 is routed through an Azure Application Gateway instance that is also used by other web apps.
You want to secure all traffic to mywebapp1 by using SSL.
Solution: You configure mywebapp1 to run in an Azure App Service Environment (ASE).
Does this meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
The Azure App Service Environment (ASE) is used to run an app in an isolated environment.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/environment/intro
NEW QUESTION 2:
HOTSPOT
You plan to deploy Windows Virtual Desktop.
Users have the devices shown in the following table.
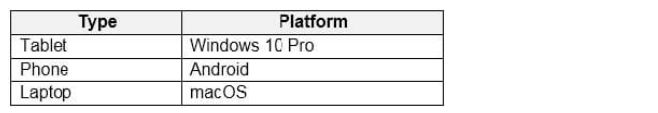
From which device types can the users connect to Windows Virtual Desktop resources by using the Remote Desktop client app and the Remote Desktop web client? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:
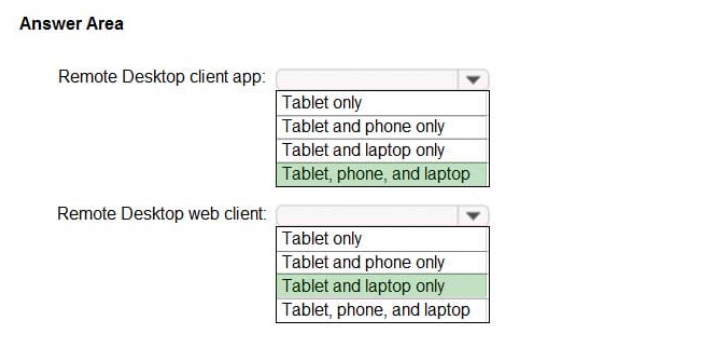
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-desktop/connect-web https://docs.microsoft.com/en-
us/azure/virtual-desktop/connect-android https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-desktop/connect-macos
NEW QUESTION 3:
Your company has a main office and two branch offices. Each office connects directly to the internet. The router in each branch office is configured as an endpoint for the following VPNs:
1.
A VPN connection to the main office
2.
A site-to-site VPN to Azure
The routers in each branch office have the Quality of Service (QoS) rules shown in the following table.
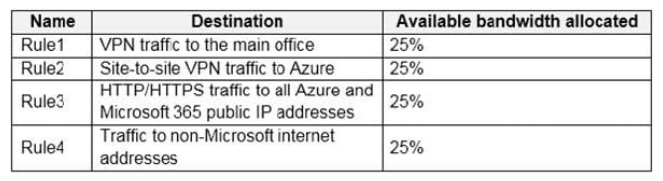
Users in the branch office report slow responses and connection errors when they attempt to connect to Windows Virtual Desktop resources.
You need to modify the QoS rules on the branch office routers to improve Windows Virtual Desktop performance.
For which rule should you increase the bandwidth allocation?
A. Rule2
B. Rule3
C. Rule4
D. Rule1
Correct Answer: B
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-desktop/rdp-quality-of-service-qos
NEW QUESTION 4:
You have an Azure Virtual Desktop deployment that contains an Azure compute gallery. The Azure compute gallery contains an image definition named Definitions Definition contains the following image versions:
1.
1.0.0
2.
1.1.0
3.
1.2.0
You need to ensure that when a virtual machine is created from the Azure compute gallery, the 1.1.0 image version is used by default.
What should you do?
A. Select Exclude from latest for image version 1.0.0.
B. Select Exclude from latest for image version 1.2.0. Most Voted
C. Apply a lock to image version 1.1.0.
D. Apply a tag named default to image version 1.1.0.
Correct Answer: B
Exclude from the latest. You can keep a version from being used as the latest image version. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/shared-image- galleries?tabs=azure-cli
NEW QUESTION 5:
Your company has a web app named WebApp1.
You use the WebJobs SDK to design a triggered App Service background task that automatically invokes a function in the code every time new data is received in a queue.
You are preparing to configure the service processes as a queue data item.
Which of the following is the service you should use?
A. Logic Apps
B. WebJobs
C. Flow
D. Functions
Correct Answer: B
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-compare-logic-apps-ms-flow-webjobs
NEW QUESTION 6:
You have an Azure Virtual Desktop deployment that contains a host pool. The host pool contains 15 session hosts. All the session hosts have FSLogix installed.
You need to configure the path to where the user profiles are stored. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
Which registry setting should you use?
A. VHDLocations
B. CCDLocations
C. ProfileDirSDDL
D. FlipFlopProfileDirectoryName
Correct Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7:
Your on-premises network contains 20 Windows 10 devices.
You have an Azure Virtual Desktop deployment.
You need to deploy the Microsoft Remote Desktop client (MSRDC) to the devices. The MSRDC must be available to everyone who signs in to the devices.
What should you do?
A. Install the MSRDC by using msiexec.exe and the ALLUSERS=1 command line option.
B. Install the MSRDC by using msiexec.exe and the ALLUSERS=2 command line option.
C. Install the MSRDC by using msiexec.exe and the MSIINSTALLPERUSER=1 command line option.
Correct Answer: A
Although your users can install the client directly after downloading it, if you\’re deploying to multiple devices, you may want to also deploy the client to them through other means. Deploying using group policies or the Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager lets you run the installer silently using a command line. Run the following commands to deploy the client per device or per user.
Per-device installation msiexec.exe /I /qn ALLUSERS=1
Incorrect: Per-user installation msiexec.exe /i “ /qn ALLUSERS=2 MSIINSTALLPERUSER=1
NEW QUESTION 8:
You have a Windows Virtual Desktop host pool that contains two session hosts. The Microsoft Teams client is installed on each session host.
You discover that only the Microsoft Teams chat and collaboration features work. The calling and meeting features are disabled.
You need to ensure that users can set the calling and meeting features from within Microsoft Teams.
What should you do?
A. Install the Remote Desktop WebRTC Redirector Service.
B. Configure Remote audio mode in the RDP Properties.
C. Install the Teams Meeting add-in for Outlook.
D. Configure audio input redirection.
Correct Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 9:
DRAG DROP
Your on-premises network contains an Active Directory domain named fabrikam.com that syncs with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). The domain contains a global group named AVDusers.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.
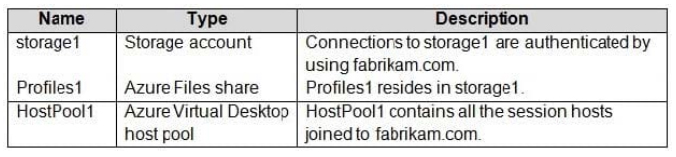
All Azure Virtual Desktop users are members of the AVDusers group.
You plan to create FSLogix profile containers in Profiles1.
You need to configure Profiles1 and fabrikam.com to ensure that the HostPool1 session hosts can access the FSLogix profile containers.
What should you do? To answer, drag the appropriate configurations to the correct targets. Each configuration may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
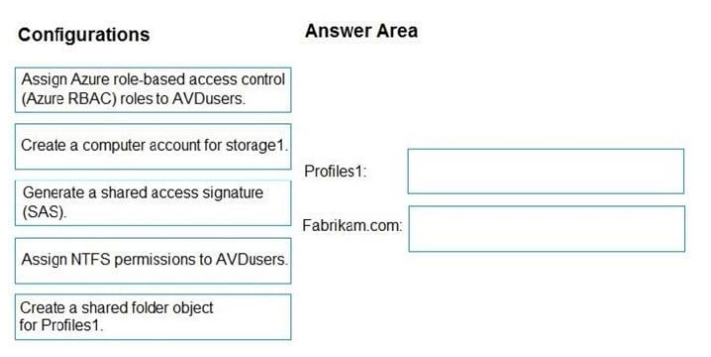
Correct Answer:
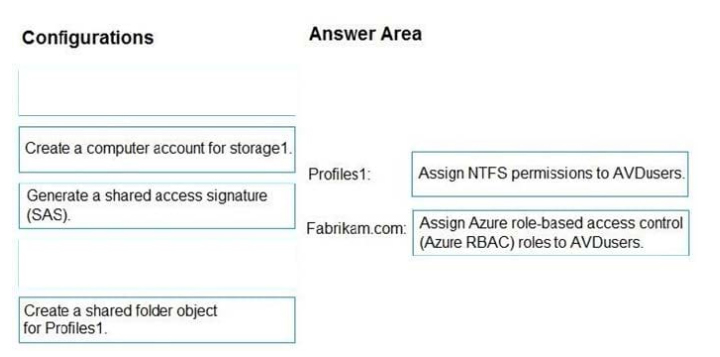
NEW QUESTION 10:
You have an Azure Active Directory Domain Services (Azure AD DS) domain named contoso.com.
You have an Azure Storage account named storage1. Storage1 hosts a file share named share1 that has share and file system permissions configured. Share1 is configured to use contoso.com for authentication.
You create an Azure Virtual Desktop host pool named Pool1. Pool1 contains two session hosts that use the Windows 10 multi-session + Microsoft 365 Apps image.
You need to configure an FSLogix profile container for Pool1.
What should you do next?
A. Install the FSLogix agent on the session hosts of Pool1.
B. From storage1, set Allow shared key access to Disabled.
C. Configure the Profiles setting for the session hosts of Pool1.
D. Generate a shared access signature (SAS) key for storage1.
Correct Answer: C
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-desktop/create-host-pools-user-profile
NEW QUESTION 11:
HOTSPOT
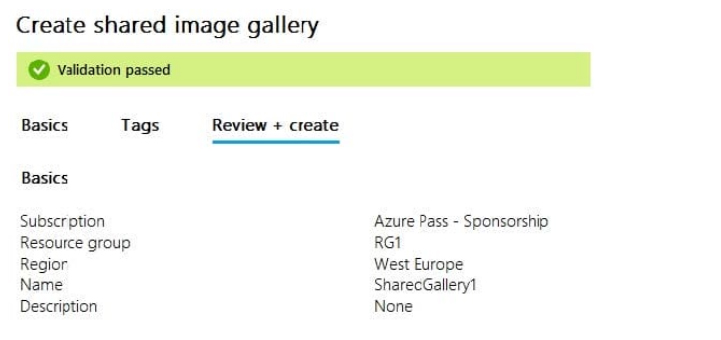
You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
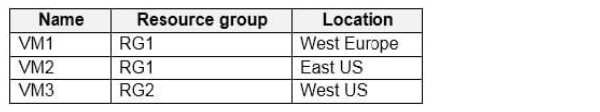
You create a shared image gallery as shown in the SharedGallery1 exhibit. (Click the SharedGallery1 tab.)
You create an image definition as shown in the Image1 exhibit. (Click the Image1 tab.)
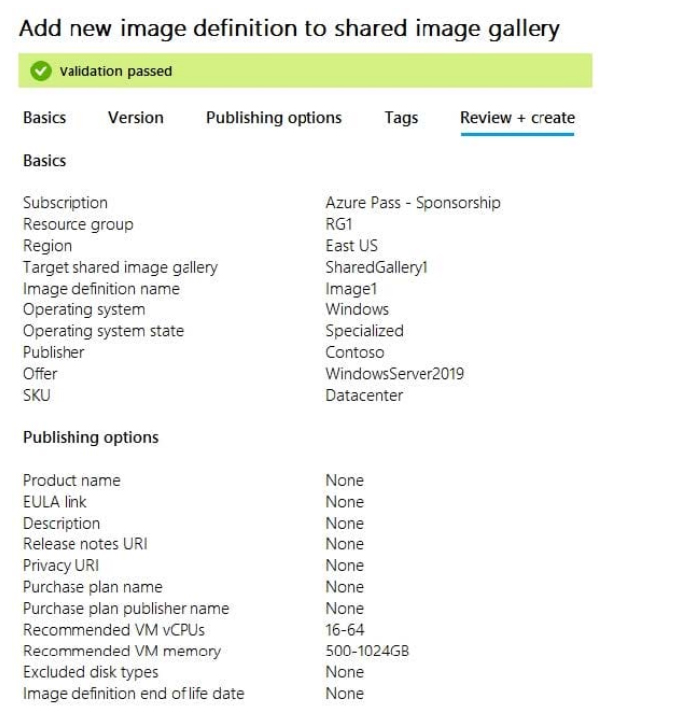
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

NEW QUESTION 12:
You have a Windows Virtual Desktop host pool named Pool1 that runs Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session hosts.
You need to use Performance Monitor to troubleshoot a low frame quality issue that is affecting a current use session to Pool1.
What should you run to retrieve the user session ID?
A. Get-ComputerInfo
B. qwinsta
C. whoami
D. Get-LocalUser
Correct Answer: B
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-desktop/troubleshoot-vm-configuration
…
Azure AZ-140 knowledge expansion
Preface:
First of all, you need to know some common Azure computing services, such as:
- Azure Virtual Machines (Azure VM), Azure Virtual Machine
- Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS), Azure’s virtual machine scale set
- Azure Container Instances (ACI), Azure’s container service
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Azure’s container orchestration service
- Azure App Services, Azure’s App Service
- Azure Functions, Azure’s function service, is also a Serverless service
Azure Virtual Machine (VM)
1.1 Introduction to Virtualization
Before introducing Azure VM, let’s briefly introduce virtualization technology in general. Assuming you have a physical server, the first step is to install the operating system and configure some system components, such as file systems, services, ports, and other settings. If you want to run multiple applications on this physical machine, you need to install these applications on the same operating system. However, in this case, these applications share the same file system, services, ports, or other configurations and may conflict. Therefore, virtualization technology emerged as the times required, which can avoid these problems.
When using virtualization technology, you need to install the operating system and virtualization software on the physical machine. Virtualization software allows you to create virtual machines that act like simulated physical machines and require their operating systems. You can host applications independently on each virtual machine’s operating system, and what those applications do on the system won’t affect applications in other virtual machines because they all run in separate virtual environments. This provides complete isolation, allowing you to virtualize multiple physical machines on a single physical machine, each with its own virtual hardware configuration and operating system.
So, virtualization is simply simulating multiple physical machines on a physical machine, allowing you to create different virtual hardware configurations and application settings for each virtual machine, and install a different operating system for each virtual machine. Now let’s discuss Azure VM further.
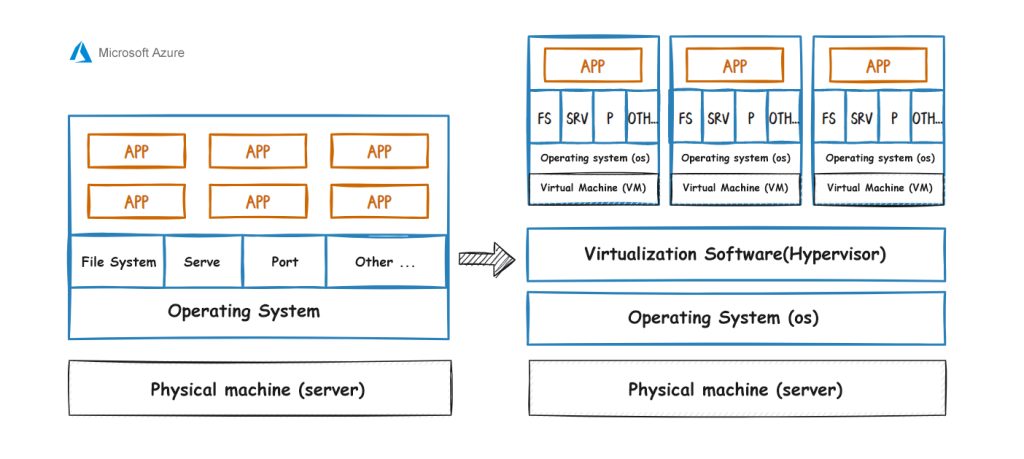
1.1.1 Key characteristics of virtualization technology
Here is a summary of several key features of virtualization technology (knock on the blackboard):
- It is a simulation technology of physical machines
- Can have different virtual hardware configurations
- Can have different operating systems
- The environment is completely separate
- File system
- Serve
- port
- middleware
- configuration etc.
1.2 Virtual machines in Azure (Azure VM)
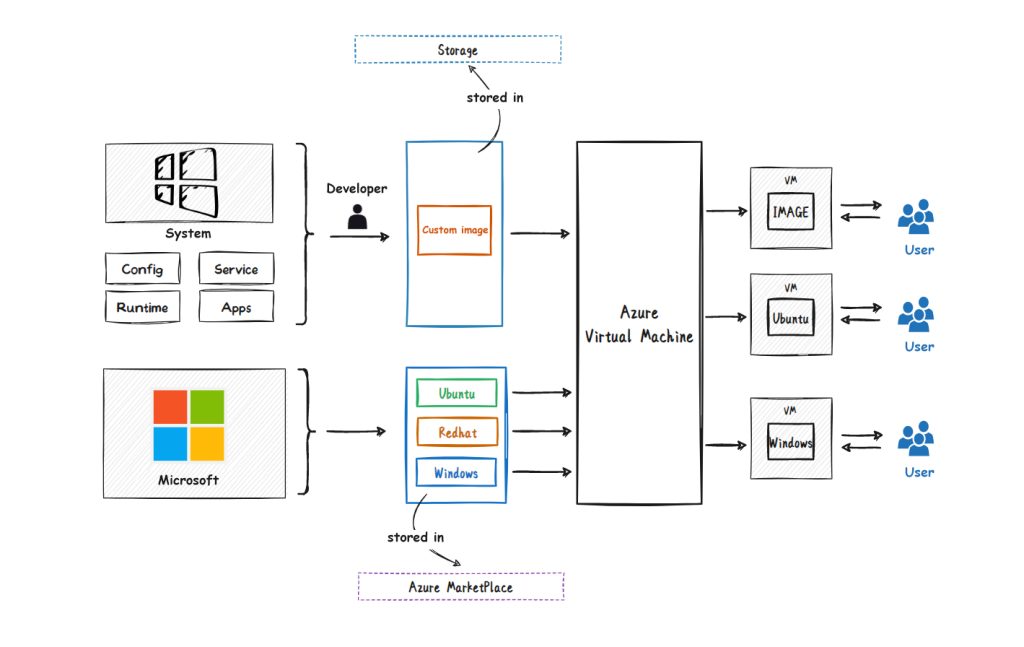
Azure Virtual Machine (VM) is a cloud-based computing resource that allows users to use virtualization technology to create and manage virtual machines in the cloud without caring about the underlying operating system and hardware. Users only need to select the required virtual machine configuration, such as CPU, memory, storage, and network, and then install their own applications and operating systems in the virtual machine to easily run their own workloads. Azure VM provides preconfigured images for a variety of operating systems and applications. Users can choose the most appropriate image to create a virtual machine according to their needs, thus greatly simplifying the management and deployment of virtual machines. Therefore, Azure VM greatly improves user productivity and reduces management and maintenance costs.
In Azure VM, Microsoft will prepare virtual machine images (Images), such as OS images for Ubuntu, Windows, Oracle, etc. Of course, you can also choose your own image and then create a VM.
The topology diagram of the service is as follows:
1.2.1 Knowledge points on key features of Azure VM
The following summarizes the key knowledge points of Azure VM (virtual machine) (typing on the blackboard is important, and will be tested in the exam)
- Azure VM (Virtual Machine) belongs to the IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) level service model
- Azure VM (Virtual Machine) is a software simulation of a physical computer.
- They include virtual processors, memory, storage, and network resources.
- They host an operating system (OS), and you can install and run software just like a physical computer.
- You can connect to the VM and control it using a remote desktop client.
- When choosing Azure VM you have the following requirements:
- Complete control over the operating system
- Requires the ability to run custom software
- Use a custom host configuration
- Azure takes care of the physical hardware
- You are responsible for configuring, updating, and maintaining the software running on the VM.
- An image is a template used to create a virtual machine.
- This includes operating systems and other software such as development tools or web hosting environments.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS)
2.1 Understanding Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (Virtual Machine Scale Sets) is an Azure service that allows users to quickly create and manage large-scale virtual machine clusters. Virtual machine scale sets provide a convenient way for users to easily expand the number of virtual machines to meet the high availability and performance needs of applications.
Virtual machine scale sets are based on virtual machine templates. Users can configure the virtual machine template according to their own needs, and then use the template to create multiple virtual machine instances. Virtual machine scale sets also provide an automatic scaling function that can automatically adjust the number of virtual machines according to actual workload conditions, thereby avoiding resource waste and performance bottlenecks.
The topology diagram of the service is as follows:
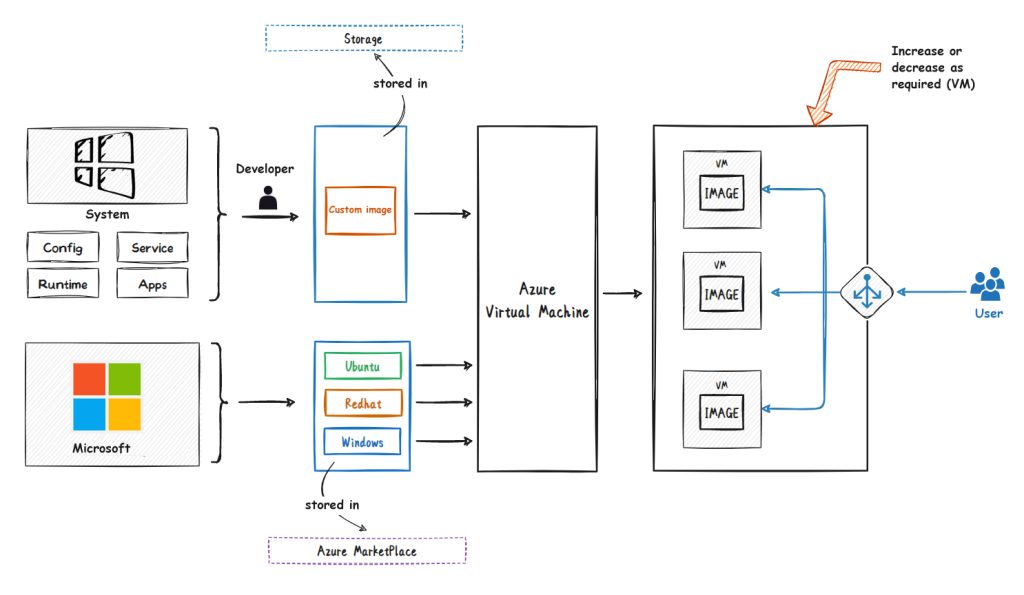
2.2 Knowledge points on key features of Azure virtual machine scale set
The following summarizes the key knowledge points of virtual machine scale sets (typing on the blackboard is important, and will be tested in the exam)
- Allows you to create and manage a group of identical, load-balanced virtual machines.
- Centrally manage, configure, and update a large number of virtual machines to provide highly available applications.
- The number of virtual machine instances can be automatically increased or decreased based on demand or a defined schedule.
- Helps you build large-scale services for areas such as computing, big data, and container workloads.
- High availability is provided through zone or multiple availability partition deployment options.
Azure Container Instance (ACI)
3.1 Introduction to containers
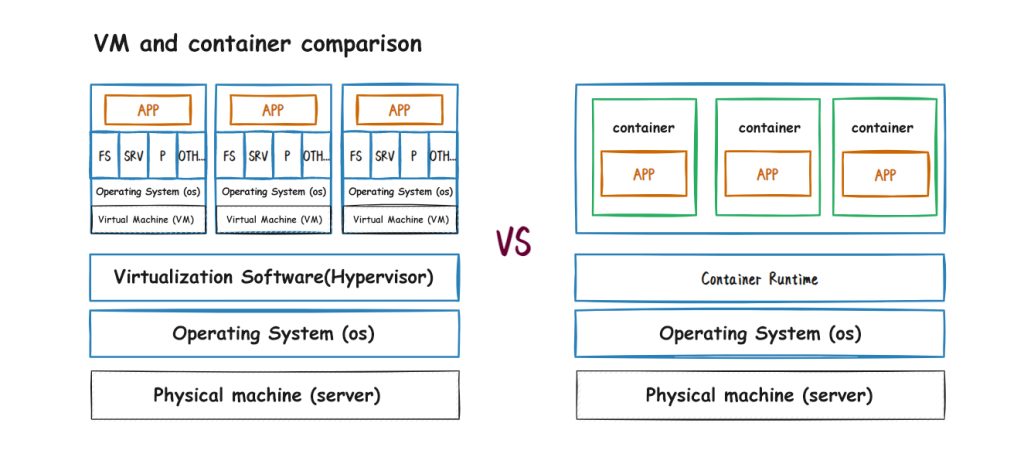
Containers are a virtualization technology that allows users to package applications and all their dependencies into an independent running environment, thereby enabling rapid deployment and portability of applications on different platforms and environments. Containers package an application and all its dependencies into a single package and provide an isolated runtime environment in which the application can run without being affected by the underlying operating system and hardware.
Unlike traditional virtual machines, containers do not require full operating system support because they share the operating system kernel. This makes containers more lightweight and efficient, starting and stopping faster. In addition, containers provide a standardized deployment method so that applications can run more stably and reliably in different environments.
Container technology has now become an important technology in the development and operation and maintenance fields. By using containers, developers can build, test, and deploy applications more quickly, and operation and maintenance personnel can more easily manage and maintain the application’s running environment, thereby improving the reliability, scalability, and flexibility of the application.
For more information about the comparison between virtual machines and containers, please refer to my previous blog post: [Cloud Native | Containers] Overview of Containers and Docker in Virtualization Technology
The topology diagram of the service is as follows:
3.2 Understanding Azure Container Instances
Azure Container Instances (ACI) is a container-oriented computing service provided by Azure that allows users to easily run Docker containers in the cloud without having to manage underlying infrastructure such as virtual machines or container orchestration engines. ACI provides a fast, lightweight, and simple way to run containers. Users only need to upload their own Docker images to ACI to quickly create and start container instances.
ACI supports a variety of container images, including Windows and Linux. Users can choose different container images to run applications and workloads according to their own needs. ACI also provides highly customizable container instance options, such as CPU, memory, storage, and network, to meet different needs. In addition, ACI also supports automatic scaling, which can automatically adjust the number of container instances according to actual workload conditions, thereby avoiding resource waste and performance bottlenecks.
The topology diagram of the service is as follows:
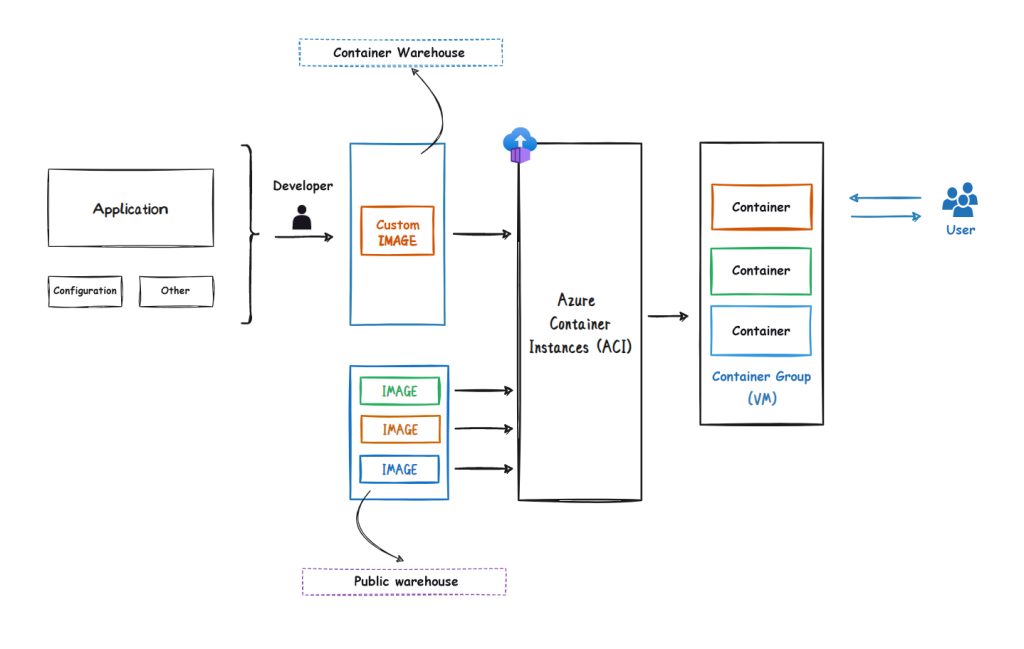
3.3 Knowledge points on key features of Azure container instances
The following summarizes the key knowledge points of Azure container instances (typing on the blackboard is important, and will be tested in the exam)
- ACI is a PaaS service
- ACI is a serverless computing service.
- ACI does not require the provisioning of virtual machines or any other additional services.
- ACI just uploads the container + runs autoscaling
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
4.1 Introduction to AKS
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a service provided by Microsoft Azure to manage Kubernetes containerized applications. It can deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters on Azure and use Azure security management, monitoring, and tracking services. It provides a fast, reliable way to deploy and manage Kubernetes containerized applications, allowing developers to focus on applications rather than managing infrastructure.
Simply put, it is a service similar to K8S provided by Microsoft.
The topology diagram of AKS services is as follows:
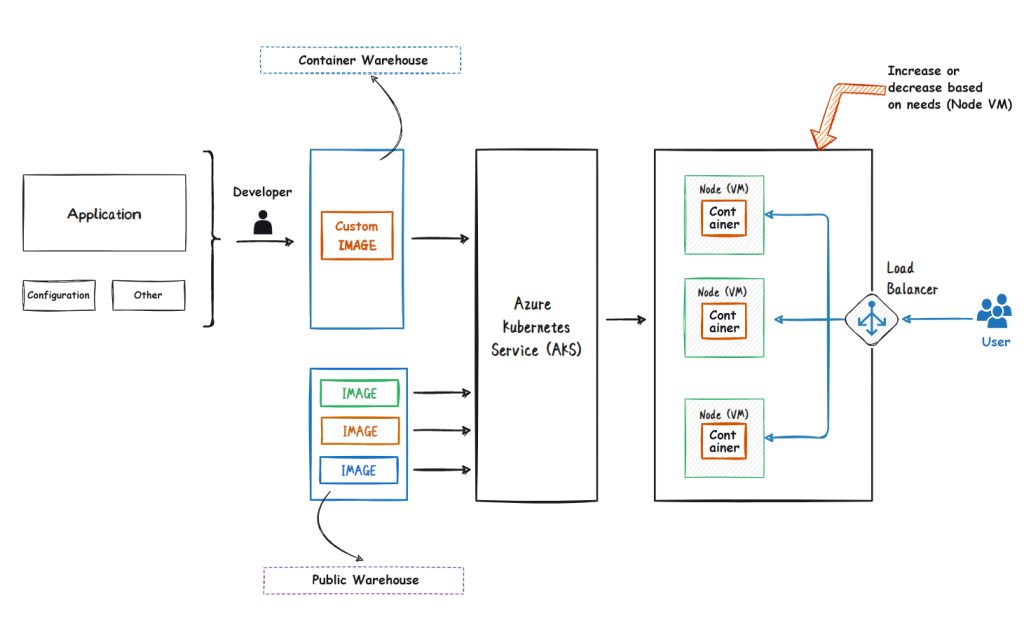
4.2 AKS key feature knowledge points
- AKS is a PaaS service.
- AKS can combine container management automation with APIs
- AKS is a cloud-native approach that can run on different clouds
- AKS Pod management:
- Manage pod storage locations
- 1 pod = 1 or more containers on a node
- If a node is removed = Kubernetes moves the affected workload to a different node.
- If a pod crashes = Kubernetes creates new instances Pods can be scaled manually or automatically (horizontally)
- AKS is a decentralized deployment that minimizes downtime and can be rolled back if there are problems with updates
- AKS can manage storage:
- Persistent volumes represent data storage in one or more containers
- Data can be persisted to multiple pod instances
- Can leverage cloud-based storage and data systems such as Azure Storage + Cosmos DB.
- AKS can manage the network:
- Can expose containers to the internet
- Can balance traffic across multiple container replicas
- Network isolation can be done
- Policy-based network security
- Manage communication and name resolution between pods
- AKS can be extended with additional features, such as cloud events on container creation, custom container scheduling logic, and on-demand access to managed cloud services.
Azure App Service
5.1 Introduction to Azure App Service
Azure App Service is a cloud service designed for building and deploying cloud applications. It enables developers to quickly develop web applications, mobile backends, and APIs in any language and framework. Applications can be deployed to Azure, and the global infrastructure can be used to manage and scale applications. Azure App Service also provides security, load balancing, and auto-scaling capabilities designed to help developers get their applications to production faster.
The topology diagram of Azure App Service is as follows:
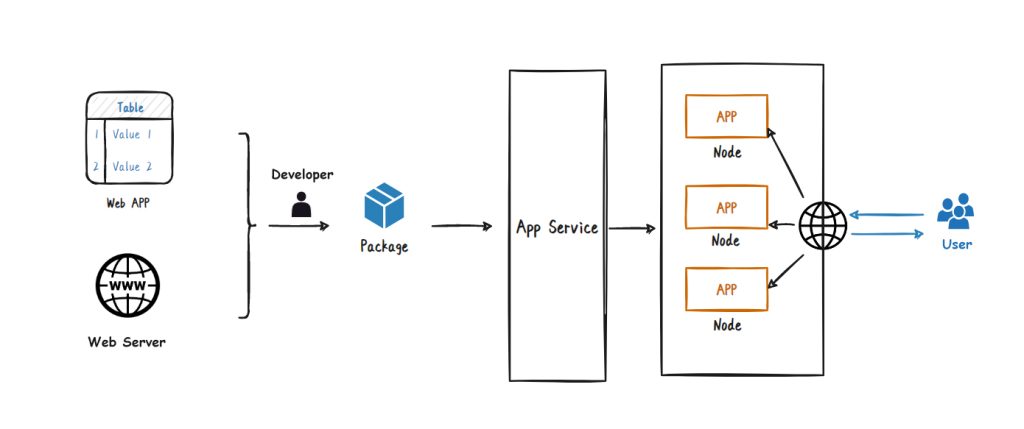
5.2 Knowledge points on key features of Azure App Service
- Azure App Service is a PaaS service.
- Azure App Service is an HTTP-based service.
- Enables you to build and host many types of web-based solutions without having to manage infrastructure.
- Web applications, mobile backends, and RESTful APIs can be hosted in a variety of supported programming languages.
- Supports different frameworks like .NET, .NET Core, Java, Ruby, Node.js, PHP, Python, etc.
- Can be extended in Windows and Linux-based environments.
Azure Functions (Function Apps)
Azure Functions (Function Apps) is an event-driven computing service that allows users to easily deploy code to the cloud to automatically execute when specific events are received. It is server-side code that can be automatically triggered when an event occurs and perform related tasks. Azure Functions (Function Apps) supports multiple programming languages, such as C#, JavaScript, Python, PHP, PowerShell, Bash, etc., which can help developers quickly implement functions.
The topology diagram of the Azure Functions service is as follows:
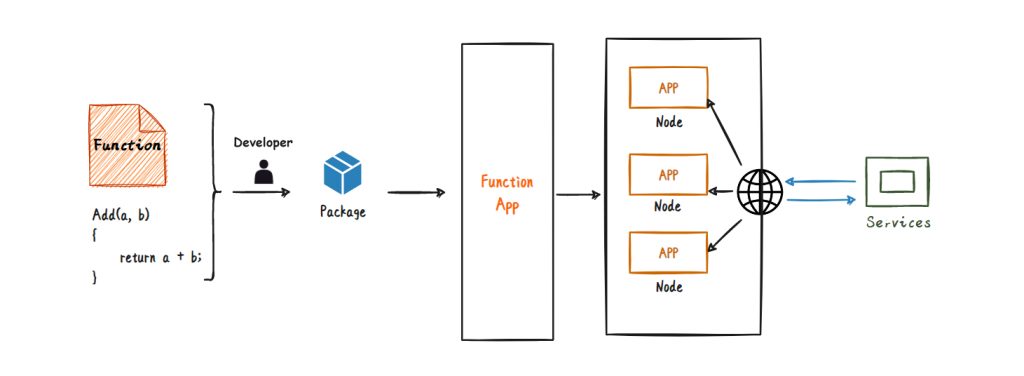
Summary of knowledge points about Azure Function:
Azure Functions can execute code in almost any modern language. Typically used when work needs to be performed in response to an event. Can be stateless (the default) which behaves like a restart every time in response to an event; stateful (called Durable Functions) which has a context that tracks previous activity.
Summarize
I have made a summary table below to facilitate your understanding:
| Exam | Skills measured | Plan |
| AZ-140 | Plan and implement an Azure Virtual Desktop infrastructure | Leads4Pass |
| Configuring and Operating Windows Virtual Desktop on Microsoft Azure | Plan and implement identity and security | |
| Microsoft Certified: Azure Virtual Desktop Specialty | Plan and implement user environments and apps | |
| Monitor and maintain an Azure Virtual Desktop infrastructure |
| Serve | Service Level | Gather |
| Virtual machine (VM) | IaaS | Customizable software, customized needs, high specialization, high degree of control |
| Virtual machine scale set (VMSS) | IaaS | Automatically scale workloads for virtual machines |
| Azure Containers (ACI) | PaaS | Simple container hosting, easy startup management |
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | PaaS | Highly scalable and customizable container hosting platform |
| Azure App Service | PaaS | Web application services provide enterprises with Web hosting functions and are easy to use. |
| Azure Functions | PaaS | It is a serverless service with a consumption-based pricing model. |