More Latest DP-100 Dumps Exam Questions->New Update Azure DP-100 Dumps Exam Questions | 2022 Real Valid: https://www.dumpsdemo.com/new-update-azure-dp-100-dumps-exam-questions-2022-real-valid/
The latest Microsoft DP-100 dumps by leads4pass help you pass the DP-100 exam for the first time! leads4pass Latest Update Microsoft DP-100 VCE Dumps and DP-100 PDF Dumps, leads4pass DP-100 Exam Questions Updated, Answers corrected! Get the latest LeadPass DP-100 dumps with Vce and PDF: https://www.leads4pass.com/dp-100.html (Q&As: 311 dumps)
[Free DP-100 PDF] Microsoft DP-100 Dumps PDF can be collected on Google Drive shared by leads4pass:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1QXv3KvzeDJVuXG6t3ug2JwblUwDGba9m/
[2022]Free Microsoft DP-100 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ERokPE8byaytg4mD7AOm74gY88zqIB-j/view?usp=sharing
[leads4pass DP-100 Youtube] 2022 Microsoft DP-100 Dumps can be viewed on Youtube shared by leads4pass
Microsoft DP-100 Online Exam Practice Questions
QUESTION 1
A set of CSV files contains sales records. All the CSV files have the same data schema.
Each CSV file contains the sales record for a particular month and has the filename sales.csv. Each file is stored in a
folder that indicates the month and year when the data was recorded. The folders are in an Azure blob container for
which a datastore has been defined in an Azure Machine Learning workspace. The folders are organized in a parent
folder named sales to create the following hierarchical structure: 
At the end of each month, a new folder with that month\\’s sales file is added to the sales folder.
You plan to use the sales data to train a machine learning model based on the following requirements:
1.
You must define a dataset that loads all of the sales data to date into a structure that can be easily converted to a
data frame.
2.
You must be able to create experiments that use only data that was created before a specific previous month, ignoring
any data that was added after that month.
3.
You must register the minimum number of datasets possible.
You need to register the sales data as a dataset in the Azure Machine Learning service workspace.
What should you do?
A. Create a tabular dataset that references the datastore and explicitly specifies each \\’sales/mm-yyyy/ sales.csv\\’ file
every month. Register the dataset with the name sales_dataset each month, replacing the existing dataset and
specifying a tag named month indicating the month and year it was registered. Use this dataset for all experiments.
B. Create a tabular dataset that references the datastore and specifies the path \\’ sales/*/sales.csv\\’, register the
a dataset with the name sales_dataset and a tag named month indicating the month and year it was registered, and use
this dataset for all experiments.
C. Create a new tabular dataset that references the datastore and explicitly specifies each \\’sales/mm- yyyy/sales.csv\\’
file every month. Register the dataset with the name sales_dataset_MM-YYYY each month with appropriate MM and
YYYY values for the month and year. Use the appropriate month- specific dataset for experiments.
D. Create a tabular dataset that references the datastore and explicitly specifies each \\’sales/mm-yyyy/ sales.csv\\’ file.
Register the dataset with the name sales_dataset each month as a new version and with a tag named month indicating
the month and the year it was registered. Use this dataset for all experiments, identifying the version to be used based on
the month tag as necessary.
Correct Answer: B
Specify the path.
Example:
The following code gets the workspace existing workspace and the desired datastore by name. And then passes the
datastore and file locations to the path parameter to create a new TabularDataset, weather_ds.
from azure ml. core import Workspace, Datastore, Dataset
datastore_name = \\’your datastore name\\’
# get an existing workspace
workspace = Workspace.from_config()
# retrieve an existing datastore in the workspace by name datastore = Datastore. get(workspace, datastore_name)
# create a TabularDataset from 3 file paths in datastore datastore_paths = [(datastore, \\’weather/2018/11.csv\\’),
(datastore, \\’weather/2018/12.csv\\’),
(datastore, \\’weather/2019/*.csv\\’)]
weather_ds = Dataset.Tabular.from_delimited_files(path=datastore_paths)
QUESTION 2
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains
a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution,
while
others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not
appear on the review screen.
You are creating a model to predict the price of a student\\’s artwork depending on the following variables:
the student\\’s length of education, degree type, and art form.
You start by creating a linear regression model.
You need to evaluate the linear regression model.
Solution: Use the following metrics: Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1 score, and AUC.
Does the solution meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
Those are metrics for evaluating classification models, instead, use: Mean Absolute Error, Root Mean Absolute Error,
Relative Absolute Error, Relative Squared Error, and the Coefficient of Determination.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/evaluate-model
QUESTION 3
You deploy a model as an Azure Machine Learning real-time web service using the following code.
The deployment fails.
You need to troubleshoot the deployment failure by determining the actions that were performed during deployment and
identifying the specific action that failed.
Which code segment should you run?
A. service.get_logs()
B. service.state
C. service.serialize()
D. service.update_deployment_state()
Correct Answer: A
You can print out detailed Docker engine log messages from the service object. You can view the log for ACI, AKS, and
Local deployments. The following example demonstrates how to print the logs.
# if you already have the service object handy print(service.get_logs())
# if you only know the name of the service (note there might be multiple services with the same name but different
version number) print(ws. webservices[\\’mysvc\\’].get_logs())
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-troubleshoot-deployment
QUESTION 4
DRAG DROP
You create a training pipeline using the Azure Machine Learning designer. You upload a CSV file that contains the data
from which you want to train your model.
You need to use the designer to create a pipeline that includes steps to perform the following tasks:
1.
Select the training features using the pandas’ filter method.
2.
Train a model based on the naive_bayes.GaussianNB algorithm.
3.
Return only the Scored Labels column by using the query SELECT [Scored Labels] FROM t1;
Which modules should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate modules to the appropriate locations. Each module
name may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to
view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place: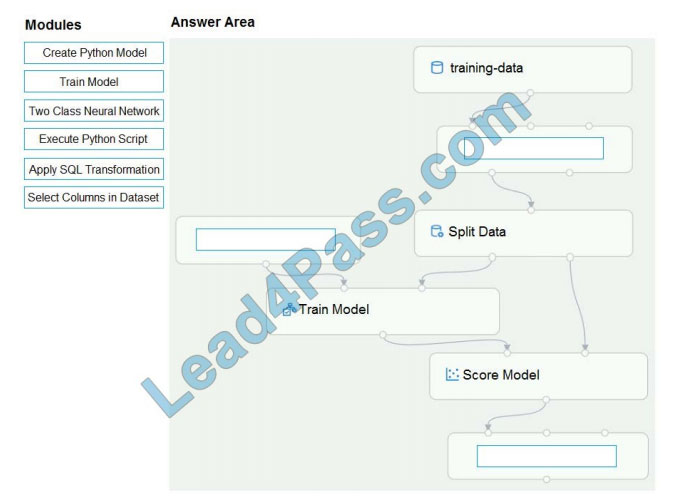
Correct Answer:
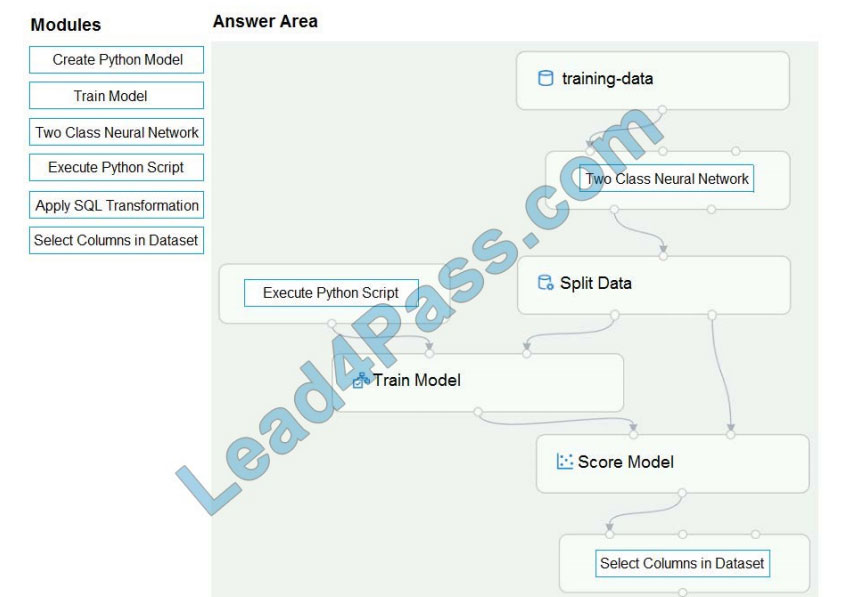
QUESTION 5
You register a file dataset named csv_folder that references a folder. The folder includes multiple comma-separated
values (CSV) files in an Azure storage blob container.
You plan to use the following code to run a script that loads data from the file dataset. You create and instantiate the
following variables: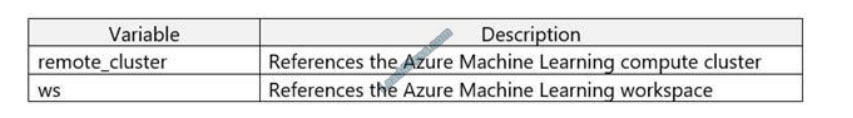
You have the following code:

You need to pass the dataset to ensure that the script can read the files it references. Which code segment should you
insert to replace the code comment?
A. inputs=[file_dataset.as_named_input(\\’training_files\\’)],
B. inputs=[file_dataset.as_named_input(\\’training_files\\’).as_mount()],
C. inputs=[file_dataset.as_named_input(\\’training_files\\’).to_pandas_dataframe ()],
D. script_params={\\’–training_files\\’: file_dataset},
Correct Answer: B
Example:
from azureml.train.estimator import Estimator
script_params = {
# to mount files referenced by mnist dataset
\\’–data-folder\\’: mnist_file_dataset.as_named_input(\\’mnist_opendataset\\’).as_mount(), \\’–regularization\\’: 0.5
}
est = Estimator(source_directory=script_folder,
script_params=script_params,
compute_target=compute_target,
environment_definition=env,
entry_script=\\’train.py\\’)
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/tutorial-train-models-with-aml
QUESTION 6
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains
a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution,
while
others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not
appear on the review screen.
You create an Azure Machine Learning service datastore in a workspace. The datastore contains the following files:
1.
/data/2018/Q1.csv
2.
/data/2018/Q2.csv
3.
/data/2018/Q3.csv
4.
/data/2018/Q4.csv
5.
/data/2019/Q1.csv All files store data in the following format: id,f1,f2,I
1,1,2,0 2,1,1,1 3,2,1,0 4,2,2,1
You run the following code: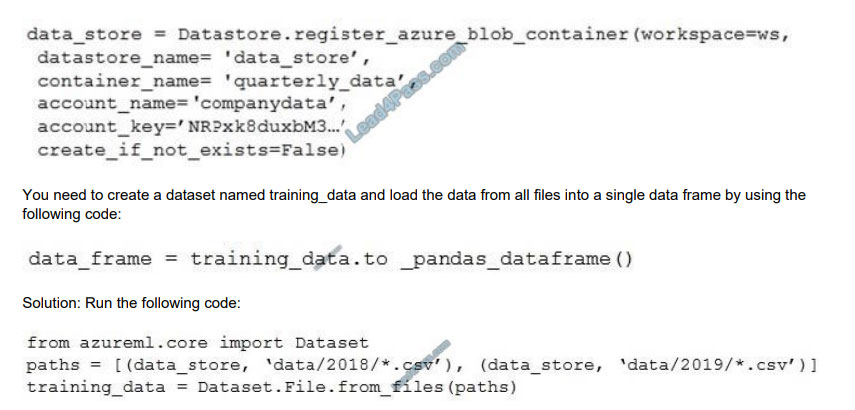
Does the solution meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
Use two file paths.
Use Dataset.Tabular_from_delimeted, instead of Dataset.File.from_files as the data isn\\’t cleansed.
Note:
A FileDataset references single or multiple files in your datastores or public URLs. If your data is already cleansed, and
ready to use in training experiments, you can download or mount the files to your compute as a FileDataset object.
A TabularDataset represents data in a tabular format by parsing the provided file or list of files. This provides you with
the ability to materialize the data into a panda or Spark DataFrame so you can work with familiar data preparation and
training libraries without having to leave your notebook. You can create a TabularDataset object from .csv, .tsv,
.parquet, .jsonl files, and from SQL query results.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-create-register-datasets
QUESTION 7
You create a multi-class image classification deep learning model that uses a set of labeled images. You create a script
file named train.py that uses the PyTorch 1.3 framework to train the model.
You must run the script by using an estimator. The code must not require any additional Python libraries to be installed
in the environment for the estimator. The time required for model training must be minimized.
You need to define the estimator that will be used to run the script.
Which estimator type should you use?
A. TensorFlow
B. PyTorch
C. SKLearn
D. Estimator
Correct Answer: B
For PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Chainer tasks, Azure Machine Learning provides respective PyTorch, TensorFlow, and
Chainer estimators to simplify using these frameworks.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-train-ml-models
QUESTION 8
HOTSPOT
You need to identify the methods for dividing the data according, to the testing requirements.
Which properties should you select? To answer, select the appropriate option-, m the answer area;
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
QUESTION 9
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains
a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution,
while
others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not
appear on the review screen.
You train a classification model by using a logistic regression algorithm.
You must be able to explain the model\\’s predictions by calculating the importance of each feature, both as an overall
global relative importance value and as a measure of local importance for a specific set of predictions.
You need to create an explainer that you can use to retrieve the required global and local feature importance values.
Solution: Create a PFIExplainer.
Does the solution meet the goal?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: A
Permutation Feature Importance Explainer (PFI): Permutation Feature Importance is a technique used to explain
classification and regression models. At a high level, the way it works is by randomly shuffling data one feature at a time
for the entire dataset and calculating how much the performance metric of interest changes. The larger the change, the
more important that feature is. PFI can explain the overall behavior of any underlying model but does not explain
individual predictions.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-machine-learning-interpretability
QUESTION 10
You create a batch inference pipeline by using the Azure ML SDK. You run the pipeline by using the following code:
from azure ml.pipeline.core import Pipeline
from azure ml. core.experiment import Experiment
pipeline = Pipeline(workspace=ws, steps=[parallelrun_step]) pipeline_run = Experiment(ws,
\\’batch_pipeline\\’).submit(pipeline)
You need to monitor the progress of the pipeline execution.
What are two possible ways to achieve this goal? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
E. Option E
Correct Answer: DE
A batch inference job can take a long time to finish. This example monitors progress by using a Jupyter widget. You can
also manage the job\\’s progress by using:
1.
Azure Machine Learning Studio.
2.
Console output from the PipelineRun object.
from azureml.widgets import RunDetails RunDetails(pipeline_run).show()
pipeline_run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True) Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-use-parallel-run-step#monitor-the-parallel-run-job
QUESTION 11
You are solving a classification task.
You must evaluate your model on a limited data sample by using k-fold cross-validation. You start by configuring a k
parameter as the number of splits.
You need to configure the k parameter for the cross-validation.
Which value should you use?
A. k=0.5
B. k=0.01
C. k=5
D. k=1
Correct Answer: C
Leave One Out (LOO) cross-validation
Setting K = n (the number of observations) yields n-fold and is called leave-one-out cross-validation (LOO), a special
case of the K-fold approach.
LOO CV is sometimes useful but typically doesn\\’t shake up the data enough. The estimates from each fold are highly
correlated and hence their average can have high variance. This is why the usual choice is K=5 or 10. It provides a
good
compromise for the bias-variance tradeoff.
QUESTION 12
You plan to create a speech recognition deep learning model.
The model must support the latest version of Python.
You need to recommend a deep learning framework for speech recognition to include in the Data Science Virtual
Machine (DSVM).
What should you recommend?
A. Rattle
B. TensorFlow
C. Weka
D. Scikit-learn
Correct Answer: B
TensorFlow is an open-source library for numerical computation and large-scale machine learning. It uses Python to
provide a convenient front-end API for building applications with the framework TensorFlow can train and run deep
neural networks for handwritten digit classification, image recognition, word embeddings, recurrent neural networks,
sequence-to-sequence models for machine translation, natural language processing, and PDE (partial differential
equation) based simulations.
Incorrect Answers:
A: Rattle is the R analytical tool that gets you started with data analytics and machine learning.
C: Weka is used for visual data mining and machine learning software in Java.
D: Scikit-learn is one of the most useful library for machine learning in Python. It is on NumPy, SciPy, and matplotlib, this
the library contains a lot of efficient tools for machine learning and statistical modeling including classification, regression,
clustering and dimensionality reduction.
Reference: https://www.infoworld.com/article/3278008/what-is-tensorflow-the-machine-learning-library-explained.html
QUESTION 13
You are retrieving data from a large datastore by using Azure Machine Learning Studio.
You must create a subset of the data for testing purposes using a random sampling seed based on the system clock.
You add the Partition and Sample module to your experiment.
You need to select the properties for the module.
Which values should you select? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: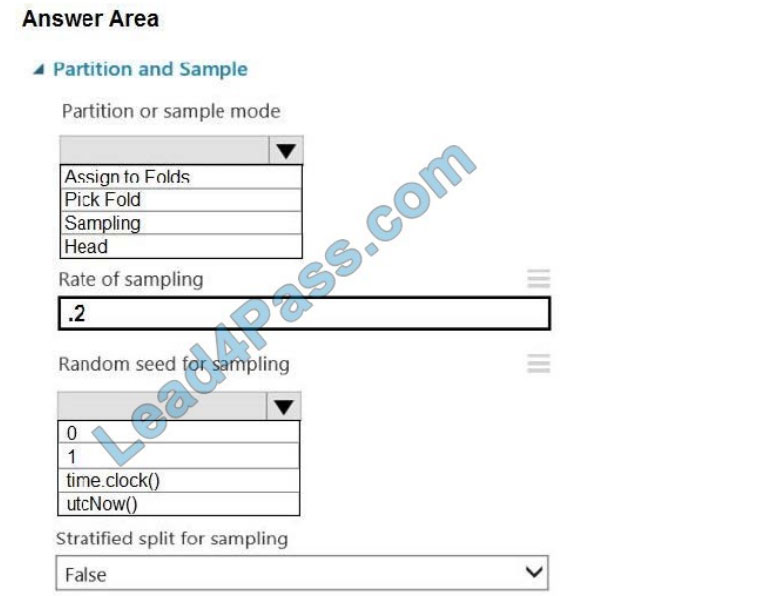
Correct Answer:
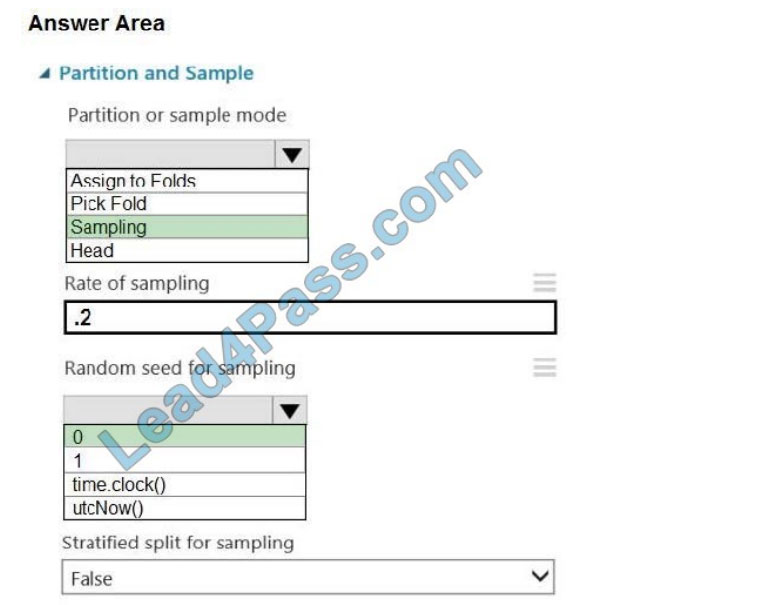
Box 1: Sampling Create a sample of data This option supports simple random sampling or stratified random sampling.
This is useful if you want to create a smaller representative sample dataset for testing.
1.
Add the Partition and Sample module to your experiment in Studio, and connect the dataset.
2.
Partition or sample mode: Set this to Sampling.
3.
Rate of sampling. See box 2 below.
Box 2: 0
3. Rate of sampling. Random seed for sampling: Optionally, type an integer to use as a seed value.
This option is important if you want the rows to be divided the same way every time. The default value is 0, meaning that
a starting seed is generated based on the system clock. This can lead to slightly different results each time you run the
experiment.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/partition-and-sample
latest updated Microsoft DP-100 exam questions from the leads4pass DP-100 dumps! 100% pass the DP-100 exam! Download leads4pass DP-100 VCE and PDF dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/dp-100.html (Q&As: 311 dumps)
Get free Microsoft DP-100 dumps PDF online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1QXv3KvzeDJVuXG6t3ug2JwblUwDGba9m/
[2022]Free Microsoft DP-100 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ERokPE8byaytg4mD7AOm74gY88zqIB-j/view?usp=sharing